Drug design, drug delivery and technologies, BioWorld Asia
Drug Design, Drug Delivery & Technologies
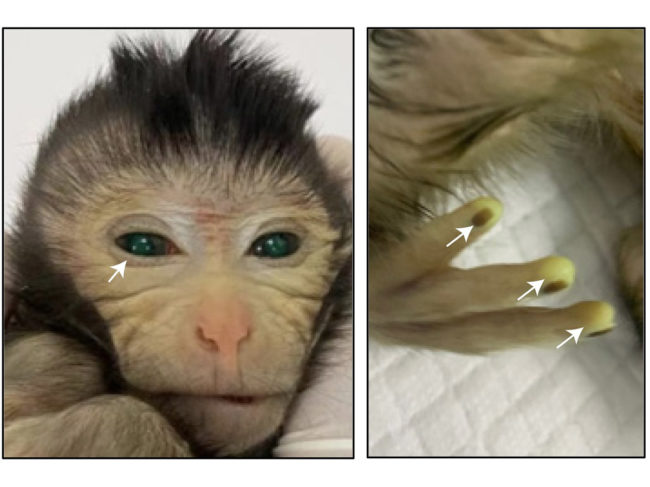
1st chimeric monkey born with large embryonic stem cell contribution
Read MoreDrug Design, Drug Delivery & Technologies
Automera launches with $16M series A funding to tackle protein degradation
Read MoreDrug Design, Drug Delivery & Technologies