Articles Tagged with ''Alzheimer’s disease''
Neurology/Psychiatric
PLD3 deletion reduces spheroid size and restores axonal conduction in AD
Read MoreNeurology/Psychiatric
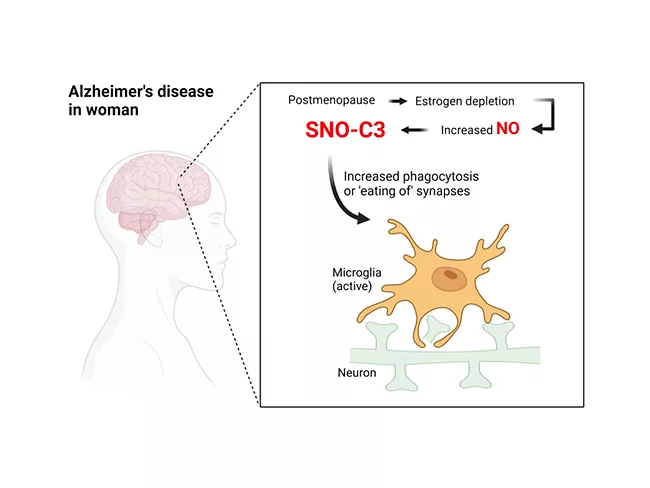
Nitric oxide-modified proteins reveal sex differences in Alzheimer’s
Read MoreNeurology/Psychiatric